Ripple and XRP: Ripple Xrp

Ripple is a technology company that provides a global financial network for cross-border payments, while XRP is a cryptocurrency that serves as a bridge currency on this network. Understanding the relationship between Ripple and XRP is crucial to comprehending the company’s mission and the role of its digital asset.
History of Ripple and XRP
Ripple’s history dates back to 2011 when it was founded by Jed McCaleb and Chris Larsen. The initial concept was a decentralized payment network called OpenCoin, which aimed to simplify and speed up cross-border transactions. The company later shifted its focus to providing enterprise-level solutions for financial institutions through RippleNet. XRP was introduced as a native digital asset on the Ripple network to facilitate these transactions.
- 2011: OpenCoin was founded, focusing on a decentralized payment network.
- 2012: The first version of the Ripple protocol was released.
- 2013: Ripple Labs was established, and XRP was introduced as a bridge currency.
- 2014: RippleNet was launched, offering enterprise solutions for financial institutions.
- 2017: XRP gained significant popularity and experienced a surge in price.
- 2018: Ripple continued to expand its network and partnerships with major financial institutions.
RippleNet and Cross-Border Payments
RippleNet is a global network that connects financial institutions, payment providers, and other businesses to facilitate cross-border payments. It offers a range of solutions, including:
- RippleNet On-Demand Liquidity: Enables financial institutions to settle payments instantly using XRP, eliminating the need for pre-funding accounts.
- RippleNet Liquidity Hub: Connects financial institutions to a network of liquidity providers, allowing them to source liquidity for cross-border payments.
- RippleNet xCurrent: Provides a messaging solution for banks to track and manage cross-border payments.
RippleNet aims to simplify and speed up cross-border payments by eliminating intermediaries, reducing transaction costs, and providing real-time tracking. This network has gained traction among financial institutions, including major banks like Santander, Standard Chartered, and Bank of America.
Technical Aspects of XRP
XRP is a cryptocurrency that operates on a decentralized, open-source blockchain. It differs from other cryptocurrencies in several ways:
- Consensus Mechanism: XRP uses a unique consensus mechanism called the “Ripple Consensus Ledger Agreement” (RCSA), which is faster and more energy-efficient than proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms. RCSA relies on a network of trusted validators to confirm transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain.
- Scalability: XRP is designed to handle a high volume of transactions per second (TPS), making it suitable for large-scale financial applications. It can process thousands of transactions per second, compared to Bitcoin’s average of seven transactions per second.
- Energy Efficiency: XRP’s consensus mechanism requires significantly less energy than PoW systems, making it more environmentally friendly.
XRP’s technical features make it a viable option for cross-border payments, offering speed, scalability, and energy efficiency. Its unique consensus mechanism and focus on enterprise solutions distinguish it from other cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory Landscape and Challenges
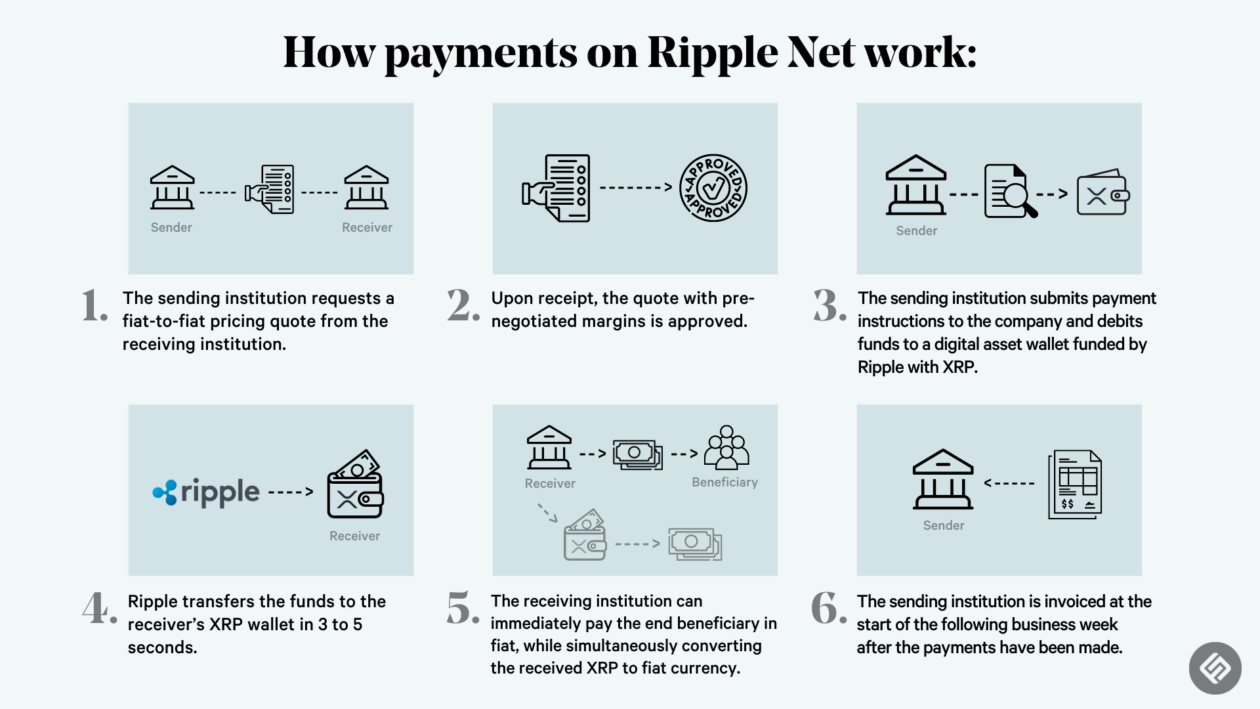
The regulatory landscape surrounding XRP is complex and evolving, with different jurisdictions taking varying approaches to its classification and oversight. This complexity has led to challenges and controversies, particularly regarding its potential classification as a security and its relationship with the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Legal Status in Different Jurisdictions, Ripple xrp
The legal status of XRP varies across different jurisdictions. Some countries, like Japan, have classified XRP as a cryptocurrency, while others, like the United States, have yet to definitively determine its legal status.
- Japan: Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA) has classified XRP as a cryptocurrency, subject to the Payment Services Act. This means that XRP exchanges and businesses dealing with XRP are required to register with the FSA and comply with relevant regulations.
- United States: The SEC has not yet definitively classified XRP. The SEC has been investigating Ripple Labs, the company behind XRP, for several years, and has alleged that XRP was sold as an unregistered security. This has created uncertainty for XRP investors and businesses operating in the US.
- European Union: The EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) applies to cryptocurrencies, including XRP. However, the specific application of MiFID II to XRP may vary depending on the individual circumstances of the transaction and the jurisdiction.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding XRP
One of the major challenges facing XRP is its classification as a security. The SEC has alleged that Ripple Labs sold XRP as an unregistered security, which would subject it to stricter regulations.
- SEC Investigation: The SEC’s investigation into Ripple Labs has been ongoing for several years, and the outcome of this investigation could have a significant impact on the future of XRP.
- Classification as a Security: The SEC’s classification of XRP as a security would mean that Ripple Labs would have to register XRP with the SEC and comply with relevant regulations. This could make it more difficult for Ripple Labs to raise capital and operate in the US.
- Investor Uncertainty: The SEC’s investigation and the potential classification of XRP as a security have created uncertainty for XRP investors, who are concerned about the potential for regulatory action and the impact on the value of their investments.
Potential Impact of Regulations on XRP’s Future
Regulations can have a significant impact on the future growth and adoption of XRP. If the SEC classifies XRP as a security, it could create challenges for Ripple Labs and make it more difficult for XRP to be adopted by businesses and consumers.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: A security classification would likely lead to increased regulatory scrutiny of XRP, which could hinder its growth and adoption.
- Impact on Liquidity: Increased regulation could also impact the liquidity of XRP, making it more difficult for investors to buy and sell the cryptocurrency.
- Potential for Adoption: However, clear and predictable regulations could also provide a foundation for greater adoption of XRP by businesses and consumers, as it would create a more stable and secure environment for its use.
Ripple XRP, like the intricate network of flight paths in the air, has experienced its share of turbulence. While the recent ground stop at NYC airports may seem unrelated, it serves as a reminder that even the most robust systems can face unexpected delays.
Just as those delays impact travelers, the regulatory uncertainty surrounding XRP has created a similar holding pattern for investors, awaiting clearer skies for the cryptocurrency to take flight.
Ripple XRP, a cryptocurrency designed for facilitating cross-border payments, has seen its fair share of volatility. Perhaps a more stable environment for its price action would be found in the quiet comfort of a dedicated workspace, like the one offered by a laptop table with chair.
After all, a focused and comfortable environment can be key to making informed decisions, whether those decisions involve investing in cryptocurrencies or simply choosing the right piece of furniture for your home office.
